Introduction of Conductor Aluminum
Conductor aluminum has become a practical substitute for a number of electrical applications, although materials like copper and silver have long dominated the field of electrical conductivity. We shall explore the characteristics of conductor aluminum to clear out why it is a good conductor aluminum. We will delve into the conductivity, affordability, resistance to corrosion, thermal performance, environmental factors, applications, and difficulties that conductor aluminum meets. By the end of this essay, you will understand why aluminum has become known as a great material for conductors.

Properties of Conductor Aluminum
Aluminum is a lightweight metal with excellent physical and chemical characteristics. It has a low density, making it importantly lighter than copper, one of the most commonly used conductors. Although its lightweight nature, conductor aluminum shows decent electrical conductivity, making it an attractive choice for conducting electricity. What’s more, conductor aluminum has excellent malleability and ductility, allowing it to be easily shaped and formed into many kinds of conductor configurations.
Conductivity of Conductor Aluminum
When discussing conductor aluminum, one of the key aspects to consider is their electrical conductivity. While conductor aluminum’s conductivity is lower than that of copper or silver, it is still sufficient for many electrical applications. In fact, conductor aluminum has approximately 61% of the electrical conductivity of copper. This means that a larger cross-sectional area of aluminum is required to achieve the same electrical conductivity as copper. However, due to aluminum’s lighter weight, it can still offer cost and performance advantages in certain scenarios.
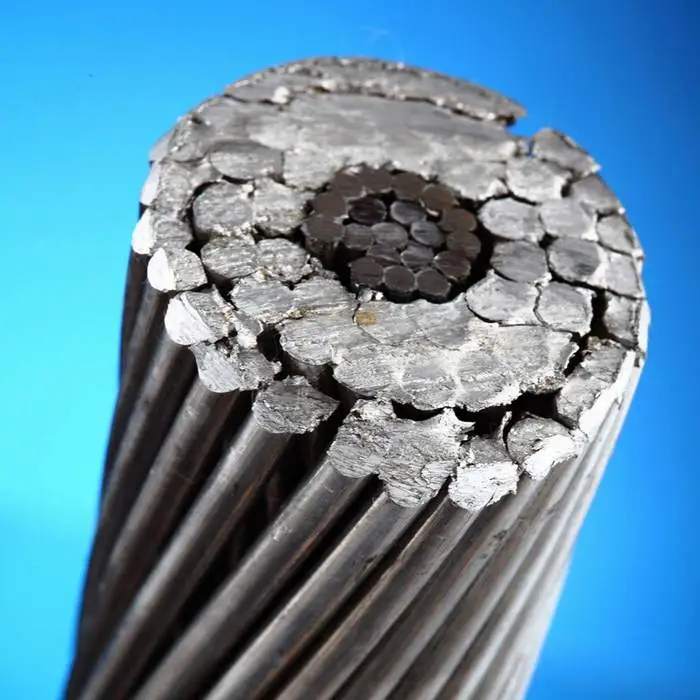

Cost-effectiveness of conductor aluminum
Conductor aluminum are known for their cost-effectiveness compared to copper conductors. Aluminum is abundantly available, making it less expensive than copper. The lower cost of conductor aluminum allows for significant savings in large-scale electrical projects, where the cost of materials can be a significant factor. Furthermore, conductor aluminum require less supporting infrastructure due to their lighter weight, reducing installation and maintenance costs.
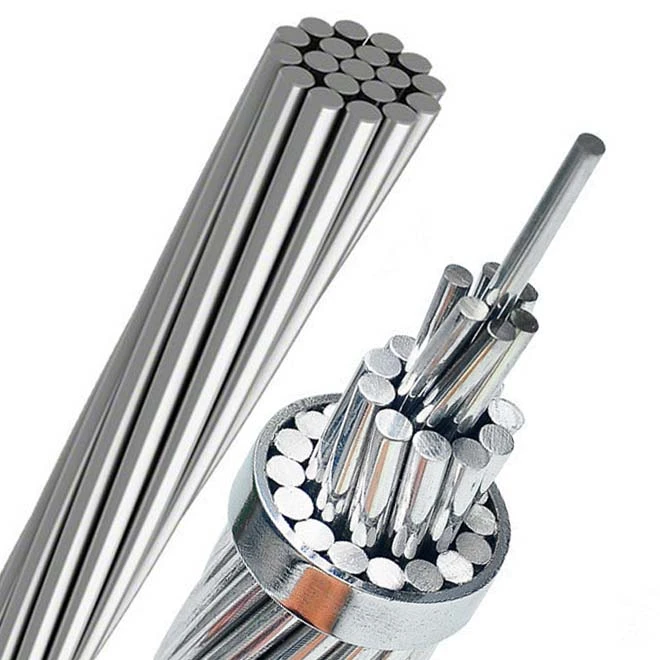

Summary
Aluminum has established itself as a practical substitute for conventional conductors such as copper. Its characteristics, encompassing conductivity, affordability, resistance to corrosion, thermal efficiency, and ecological aspects, render it an appealing option for aluminum conductors. Although aluminum does present certain obstacles and restrictions, they can be overcome by employing appropriate engineering and installation methodologies. As the global pursuit of sustainable and effective solutions persists, aluminum conductors will assume a vital position in the advancement of electrical systems. They will facilitate dependable power transmission and distribution while enhancing cost efficiency and promoting environmental sustainability.



 Loading
Loading













